ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE
Organizational culture refers to a system of shared meaning held by
members that distinguishes the organization from other organizations or the
behaviors that is meaningful to people.
Healthy
Organizations should consider “healthy”
organizational culture in order to increase growth, efficiency and
productivity. Some characteristics describe a healthy culture here are the some
of them:
· Acceptance and appreciation for
diversity
· Employee’s contribution to the company
· Equal opportunity for each employee to
realize their full potential within the company
· Strong company leaders with a strong
sense of direction and purpose
Performance oriented cultures have been statistically better than
financial growth. Some cultures possess strong internal communications, high
employee involvement and encouragement of a healthy level of risk-taking in
order to achieve innovation.
According to Kotter and Heskett, organizations
with adaptive cultures perform much better than organizations with non-adaptive
cultures. An adaptive culture translates into organizational success; it is
characterized by managers paying close attention to all of their
constituencies, especially customers, initiating change when needed, and taking
risks. A non-adaptive culture can significantly reduce a firm's effectiveness,
disabling the firm from pursuing all its competitive/operational options.
Because organizational cultures affect the people’s work performance.
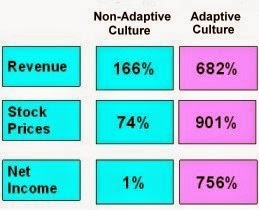
As we
see from the table, adaptive cultures are very advantageous than non-adaptive
culture revenues, prices and net incomes are very different.
Charles Handy
Charles Handy popularized with linking organizational structure to
organizational culture. According to him, there are four types of cultures:
1.
Power culture: Power cultures need only a few rules and little bureaucracy but swift in decisions can ensue.
2.
Role culture: These organizations
form hierarchical bureaucracies, where power derives from the personal position
and rarely from an expert power. These organizations have consistent systems
and are very predictable.
3.
Task culture: Power is derived from
the team with the expertise to execute against a task. This culture uses a
small team approach, where people are highly skilled and specialized in their
own area of expertise.
4.
Person culture: Formed where all individuals believe themselves superior to
the organization. It can become difficult for such organizations to continue to
operate.
Kim Cameron and
Robert Quinn
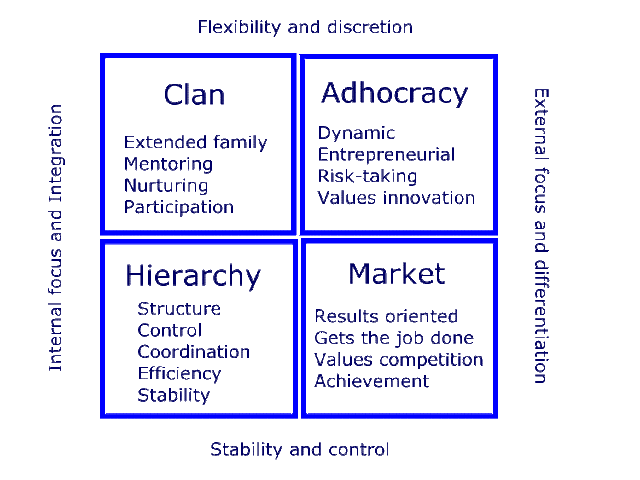
Kim Cameron and Robert Quinn conducted research on
organizational effectiveness and success. They developed the Organizational
Culture Assessment Instrument that distinguishes four culture types. Four types
of cultures are:
·
Clan culture (internal focus and
flexible) - A friendly workplace
·
Adhocracy culture (external focus and
flexible) - A dynamic workplace
·
Market culture (external focus and controlled) - A competitive
workplace
·
Hierarchy culture (internal focus and controlled) - A structured
and formalized workplace
Robert A. Cooke
Robert A. Cooke
defines culture as the behaviors that members believe are required to fit in
and meet expectations within their organization. The Organizational Culture
Inventory measures twelve behavioral norms that are grouped into three general
types of cultures:
·
Constructive cultures, in which members are encouraged to
interact with people and approach tasks in ways that help them meet their higher-order
satisfaction needs.
·
Passive/defensive cultures, in which members believe they must
interact with people in ways that will not threaten their own security.
·
Aggressive/defensive cultures, in which members are expected to
approach tasks in forceful ways to protect their status and security.
Constructive Cultures
In constructive
cultures people are encouraged to be in communication with their co-workers,
and work as teams, rather than only as individuals.
1.
Achievement: completing a task successfully, typically by effort, courage,
or skill
2.
Self-actualizing: realization or fulfillment of one's talents and potentialities
3.
Humanistic-encouraging: help others to grow and develop
4.
Affiliate: treat people as more valuable than things
Organizations with
constructive cultures encourage members to work to their full potential,
resulting in high levels of motivation, satisfaction, teamwork, service
quality, and sales growth.
Passive/Defensive Cultures
Norms that
reflect expectations for members to interact with people in ways that will not
threaten their own security are in the Passive/Defensive Cluster.
The four Passive/Defensive cultural norms are:
·
Approval
·
Conventional
·
Dependent
·
Avoidance
In organizations
with Passive/Defensive cultures, members feel pressured to think and behave in
ways that are inconsistent with the way they believe they should in order to be
effective. People are expected to please others (particularly superiors) and
avoid interpersonal conflict.
Aggressive/Defensive Cultures
This style is
characterized with more emphasis on task than people.
1.
Oppositional - This cultural norm is based on the idea that a need for
security that takes the form of being very critical and cynical at times.
2.
Power - This cultural norm is based on the idea that there is a
need for prestige and influence.
3.
Competitive - This cultural norm is based on the idea of a need to
protect one’s status.
4.
Perfectionistic - This cultural norm is based on the need to attain
flawless results.
Organizations
with aggressive/defensive cultures encourage or require members to appear
competent, controlled, and superior. Members who seek assistance, admit
shortcomings, or concede their position are viewed as incompetent or weak.
Entrepreneurial
An Entrepreneurial
Organizational Culture (EOC) is a system of shared values, beliefs and norms of
members of an organization, including valuing creativity and tolerance of
creative people, believing that innovating and seizing market opportunities are
appropriate behaviors to deal with problems of survival and prosperity,
environmental uncertainty, and competitors' threats, and expecting
organizational members to behave accordingly.
Elements
·
People and empowerment focused
·
Value creation through innovation and change
·
Attention to the basics
·
Hands-on management
·
Doing the right thing
·
Freedom to grow and to fail
·
Commitment and personal responsibility
·
Emphasis on the future
Tribal Culture
Identify five basic stages:
Bullying Culture
Bullying is seen to be prevalent in organizations where employees and managers feel that they have the support, or at least implicitly the blessing, of senior managers to carry on their abusive and bullying behavior.
Impacts
Research
suggests that numerous outcomes have been associated either directly or
indirectly with organizational culture. A healthy and robust organizational
culture may provide various benefits:
·
Competitive edge derived from innovation and customer service
·
Consistent, efficient employee performance
·
Team cohesiveness
·
High employee morale
·
Strong company alignment towards goal achievement
Mergers and
Cultural Leadership
One of the
biggest obstacles in the way of the merging of two organizations is
organizational culture. Each organization has its own unique culture, when
brought together, these cultures clash. When mergers fail employees point to
issues such as identity, communication problems, human resources problems, ego
clashes, and inter-group conflicts, which all fall under the category of
"cultural differences”. Cultural innovation followed by cultural
maintenance.
·
Cultural innovation
·
Cultural maintenance
·
Integrating the new culture
·
Embodying the new culture
Corporate Subcultures
Corporate culture is the total sum of the
values, customs, traditions, and meanings that make a company unique. Corporate
culture is often called "the character of an organization", since it
embodies the vision of the company's founders. The values of a corporate
culture influence the ethical standards within a corporation, as well as
managerial behavior.
Critical Views
Criticism of the usage of the
term by managers began already in its emergence in the early 80s. Most of
the criticism comes from the writers in studies
who for example express skepticism
about the functionalist views about culture that are put forward by mainstream management writers. They stress the ways in
which these cultural assumptions can stifle dissent management and reproduce
propaganda and ideology. They suggest that organizations do not have a single
culture and cultural engineering may not reflect the interests of all
stakeholders within an organization.




Derya explained the topic very clear and understandable I want to add something about this topic.
YanıtlaSilCorporate culture can legally be found to be a cause of injuries and a reason for fining companies in the US, e.g., when the US Department of Labor Mine Safety and Health Administration levied a fine of more than 10.8 million US dollars on Performance Coal Co. following the Upper Big Branch Mine disaster in April 2010. This was the largest fine in the history of this U.S. government agency.
.It is very well- organized and clear text. According to my determination, all the main points are placed in your text, but this information has may been added,
YanıtlaSilCulture of Fear: Several studies have confirmed a relationship between bullying, on the one hand, and an autocratic leadership and an authoritarian way of settling conflicts or dealing with disagreements, on the other.
Your wiritng plan helps the people who read your blog understand easily the topic. You explained different people's different types of cultures and explained them. You also mentioned about their elements I mean you explained everything very detailed, almost :) In my humble opinion, if you had mentioned about ''Culture Development'' and ''Key Factors that Affect Culture Development'' that would be nice,and last thing that using it could be useful for you;
YanıtlaSilPersonal Culture
Organizational culture is taught to the person as culture is taught by his/her parents thus changing and modeling his/her personal culture.